Intel Core i9-9900K CPU Review: 8-Core 9th Gen Coffee Lake Benchmarks
Intel Core i9-9900K Processor Details, Speeds, and Feeds
After what seemed like months of leaks and speculation, Intel officially announced its 9th Generation Core desktop CPU line-up a couple of weeks back, at a lavish event in New York City. Though the upcoming Core X series processors, the beastly 28-core Xeon W-3175X, and the 9th Gen Core i family don’t feature new architectures, all of the parts bring something fresh to the table, whether it be soldered thermal interface material, unlocked multipliers in the case of the Xeon, or updated silicon designs that incorporate more core resources, among other things.
One of the most anticipated and talked about of the new processors is the Core i9-9900K we’ll be showing you here today. Intel has billed the Core i9-9900K as the "best CPU for gaming" yet, thanks to its relatively high clocks and monolithic 8-core / 16-thread design with additional cache. A couple more cores and higher clocks than its predecessors aren’t the Core i9-9900K’s only tricks, however. This new processor is also the first in Intel’s line-up to feature some hardware-level fixes for certain variants of the Spectre, Meltdown, and L1TF exploits that caused such a fuss a few months back, and it arrives alongside a new chipset as well that packs in a couple of useful features.
Here’s a quick breakdown of the new 9th Generation Core processors, along with some additional specifics about the Core i9-9900K in particular. Take a peek at the new product stack and then we’ll dig in deeper and see what Intel’s new speed demon is all about...

There are some interesting things to see in the table above; notice the Core i9-9900K boasts a maximum Turbo Boost frequency of 5.0GHz. Its base clock is 3.6GHz and the processor is packing 8 cores with HyperThreading support for 16 total threads. The Core i9-9900K also features 16MB of Intel Smart Cache that’s accessible by all of the cores, 16-lanes of on-processor PCIe connectivity (with additional lanes coming by way of the chipset), official support (without overclocking) for dual-channel memory speeds of up to DDR4-2666, and it has a 95 watt TDP.
The Core i7-9700K is also an 8 core processor, but it lacks HyperThreading, is clocked slightly lower, and has 4MB of smart cache disabled. The Core i5-9600K takes things down to 6 cores / 6 threads, with a higher base clock, but lower boost clock and only 9MB of smart cache. It’s interesting that Intel disabled HT on a relatively high-end Core i7 processor, but we suspect it did so to potentially leave some wiggle room in the stack for additional processors down the line and to reduce power consumption.
As we mentioned, we’ve got the Core i9-9900K on hand here for testing. The Core i9-9900K is designed for Intel’s socket 1151, just like 8th Gen parts, and it will work on existing 300-series chipset based motherboards, provided they’ve got the proper BIOS support. We’d suggested sticking only with high-end, enthusiast-class boards with this processor, though. First, all of Intel’s K-SKU processors are unlocked for easier overclocking, but you’ll lose overclocking support on lower-end boards. Second, for best overall performance, the Core i9-9900K requires clean, constant power, and plenty of it, and some lower-end boards may not have the chops to keep the 9900K properly fed. Many of the new Z390-based motherboards that are arriving alongside the Core i9-9900K have beefier power circuitry that are purpose-built for the new chips.
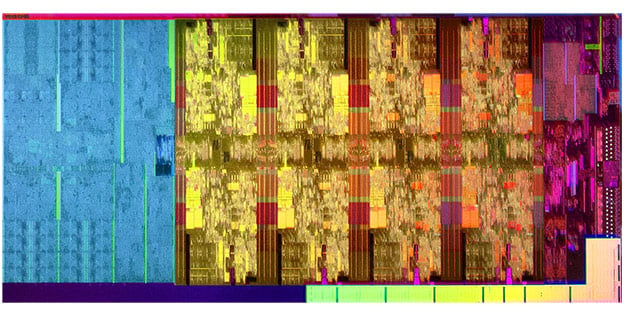
Although the Core i9-9900K looks just like previous-gen socket 1151 processors, there are some differences under that heat spreader too. Of course, there’s the new, Coffee Lake-based monolithic 8-core die that’s being manufactured on Intel’s 14nm++ process, but there’s also solder thermal interface material (STIM) to make heat transfer more efficient. Intel ditched solder TIM years ago in favor of a less-efficient, cheaper, and easier to manufacture thermal paste, but the company is bringing back solder TIM on its latest enthusiast processors. Using solder TIM will improve thermals over the less efficient paste and ultimately bring die temps down and help with overclockability.
We should also mention again that the 9th Gen Intel Core family processors are the first to feature silicon-level fixes for a couple of the Spectre, Meltdown, and L1TF exploits. While most of the variants will continue to be addressed via microcode and software patches for now, 9th Gen Core processors fix the speculative side channel L1 Terminal Fault and Meltdown V3 (Rogue Data Cache Load) vulnerabilities in hardware.
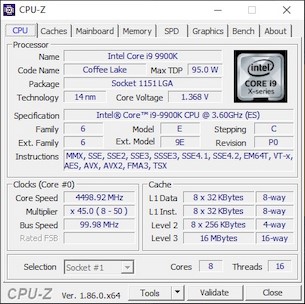
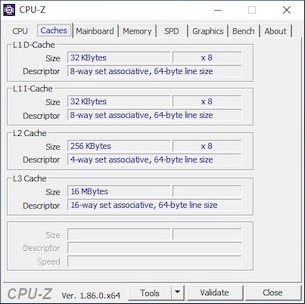
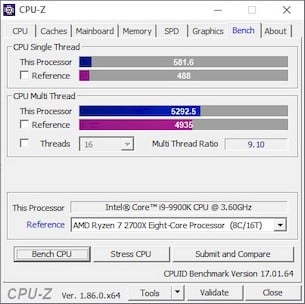
The Core i9-9900K’s CPU-Z details are outlined in the images above. We snapped the images with a single-core under load and again with 100% of the CPU being utilized. You can see that 5GHz boost clock with a single-core under load, and all cores would boost to 4.7GHz briefly, but fluctuated between 4.5 - 4.7GHz.
One of the most anticipated and talked about of the new processors is the Core i9-9900K we’ll be showing you here today. Intel has billed the Core i9-9900K as the "best CPU for gaming" yet, thanks to its relatively high clocks and monolithic 8-core / 16-thread design with additional cache. A couple more cores and higher clocks than its predecessors aren’t the Core i9-9900K’s only tricks, however. This new processor is also the first in Intel’s line-up to feature some hardware-level fixes for certain variants of the Spectre, Meltdown, and L1TF exploits that caused such a fuss a few months back, and it arrives alongside a new chipset as well that packs in a couple of useful features.
Here’s a quick breakdown of the new 9th Generation Core processors, along with some additional specifics about the Core i9-9900K in particular. Take a peek at the new product stack and then we’ll dig in deeper and see what Intel’s new speed demon is all about...
|

Intel Core i9-9900K Processor Key Features
|
There are some interesting things to see in the table above; notice the Core i9-9900K boasts a maximum Turbo Boost frequency of 5.0GHz. Its base clock is 3.6GHz and the processor is packing 8 cores with HyperThreading support for 16 total threads. The Core i9-9900K also features 16MB of Intel Smart Cache that’s accessible by all of the cores, 16-lanes of on-processor PCIe connectivity (with additional lanes coming by way of the chipset), official support (without overclocking) for dual-channel memory speeds of up to DDR4-2666, and it has a 95 watt TDP.
The Core i7-9700K is also an 8 core processor, but it lacks HyperThreading, is clocked slightly lower, and has 4MB of smart cache disabled. The Core i5-9600K takes things down to 6 cores / 6 threads, with a higher base clock, but lower boost clock and only 9MB of smart cache. It’s interesting that Intel disabled HT on a relatively high-end Core i7 processor, but we suspect it did so to potentially leave some wiggle room in the stack for additional processors down the line and to reduce power consumption.
As we mentioned, we’ve got the Core i9-9900K on hand here for testing. The Core i9-9900K is designed for Intel’s socket 1151, just like 8th Gen parts, and it will work on existing 300-series chipset based motherboards, provided they’ve got the proper BIOS support. We’d suggested sticking only with high-end, enthusiast-class boards with this processor, though. First, all of Intel’s K-SKU processors are unlocked for easier overclocking, but you’ll lose overclocking support on lower-end boards. Second, for best overall performance, the Core i9-9900K requires clean, constant power, and plenty of it, and some lower-end boards may not have the chops to keep the 9900K properly fed. Many of the new Z390-based motherboards that are arriving alongside the Core i9-9900K have beefier power circuitry that are purpose-built for the new chips.
Although the Core i9-9900K looks just like previous-gen socket 1151 processors, there are some differences under that heat spreader too. Of course, there’s the new, Coffee Lake-based monolithic 8-core die that’s being manufactured on Intel’s 14nm++ process, but there’s also solder thermal interface material (STIM) to make heat transfer more efficient. Intel ditched solder TIM years ago in favor of a less-efficient, cheaper, and easier to manufacture thermal paste, but the company is bringing back solder TIM on its latest enthusiast processors. Using solder TIM will improve thermals over the less efficient paste and ultimately bring die temps down and help with overclockability.
We should also mention again that the 9th Gen Intel Core family processors are the first to feature silicon-level fixes for a couple of the Spectre, Meltdown, and L1TF exploits. While most of the variants will continue to be addressed via microcode and software patches for now, 9th Gen Core processors fix the speculative side channel L1 Terminal Fault and Meltdown V3 (Rogue Data Cache Load) vulnerabilities in hardware.
The Core i9-9900K’s CPU-Z details are outlined in the images above. We snapped the images with a single-core under load and again with 100% of the CPU being utilized. You can see that 5GHz boost clock with a single-core under load, and all cores would boost to 4.7GHz briefly, but fluctuated between 4.5 - 4.7GHz.